OPS145 Lab 6 Newversion: Difference between revisions
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
* Since you're at it: here's a new command. Run '''history''' on the terminal. It will show you all the previous commands you've run. | * Since you're at it: here's a new command. Run '''history''' on the terminal. It will show you all the previous commands you've run. | ||
== * | == The * wildcard == | ||
You've used the '''*''' wildcard (called a star, it's the multiplication sign on your keyboard) in [[OPS145 Lab 3#Deleting files|lab 3]] to delete several files at the same time. Now we'll look at it in more detail. | You've used the '''*''' wildcard (called a star, it's the multiplication sign on your keyboard) in [[OPS145 Lab 3#Deleting files|lab 3]] to delete several files at the same time. Now we'll look at it in more detail. | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 26 February 2024
Special characters in the shell
The terminal you've been using this whole time in the course is running an application called the shell. Specifically the bash shell.
This application (bash) has been written to interpret input from the user as some sort of a command; or as an argument; or as data. It's a very powerful application with many abilities, but almost all the user input comes from the keyboard.
There are only so many keys of the keyboard, and most of them are used to input human-readable characters. That means some of those characters will necessarily have multiple meanings. We will look at several such characters in this lab.
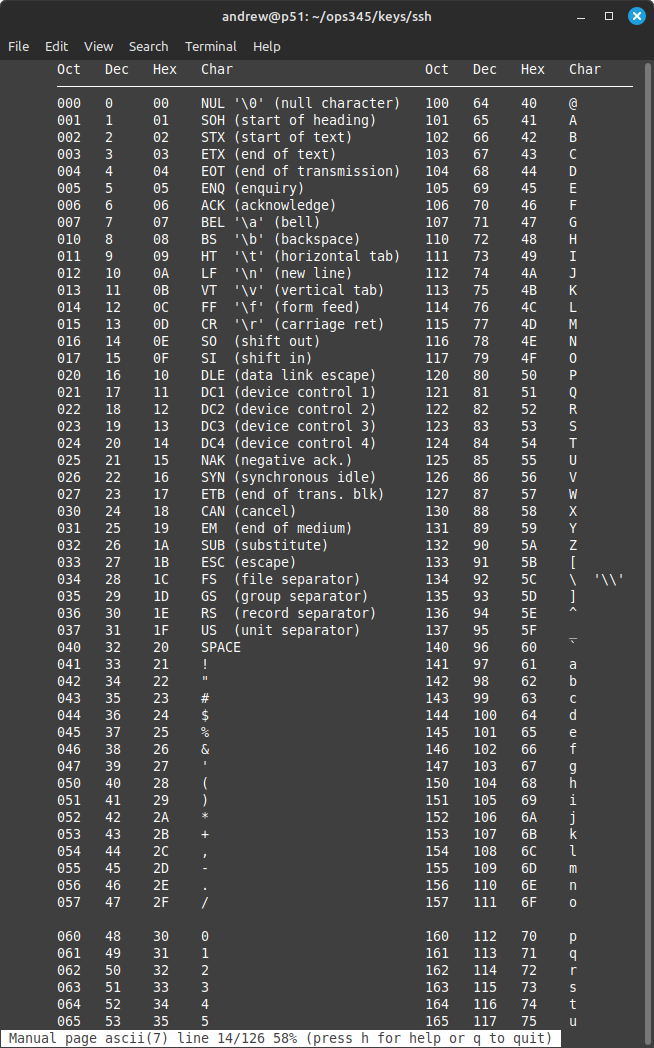
Here's most of the ASCII table (as much as I could fit on my screen). Note that most of the characters in this table are familiar to you, but some (especially the first 32) are probably brand new to you. You can see this table easily by running man ascii:
. and ..
Coming from the Windows world you might be used to the concepts of "filename" and "extension". If you're not too familiar with that: you should configure your windows to always show file extensions (it doesn't by default).
For example if you have a picture file called smily.jpg: You might call smily the filename, and jpg the extension. But then what is the dot? You could call it a separator, but In fact the dot is just as much part of the filename as smily and jpg. Looking at the ASCII table: s and m are just as different from each other as s and .
And what's the extension in a file called lab1.tar.xz? Is it xz? Or tar.xz? What about in a file called Dr. Evil plan.txt?
When it comes to filenames and extensions: the use of a dot as a separator is just a convention to help people organize their files, and is barely useful from a technological point of view.
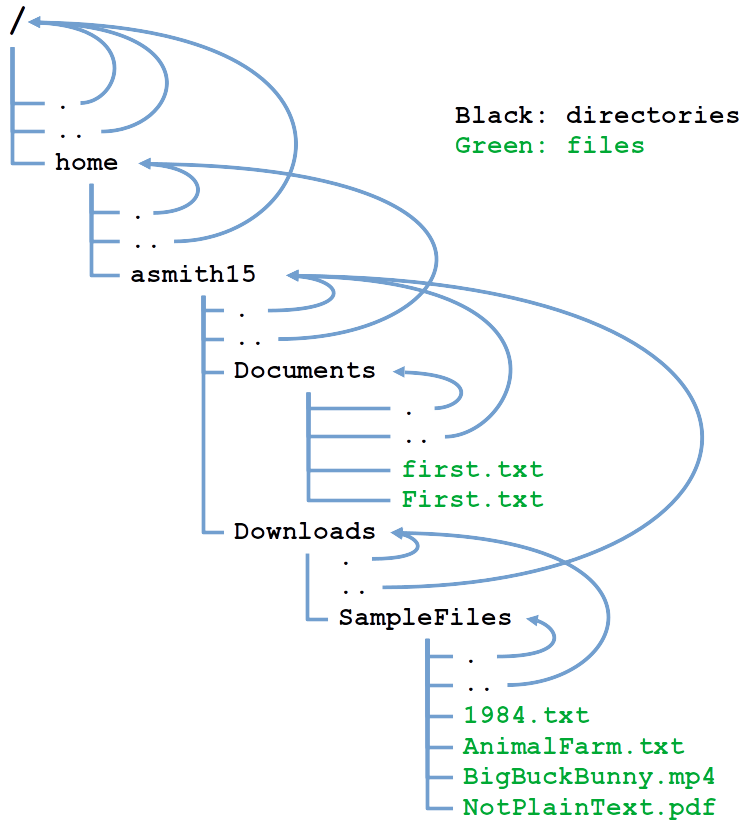
But there's another use of dots in filesystems, which is much more fundamental. Every directory contains at least these two records: a link to itself (.), and a link to its parent (..)
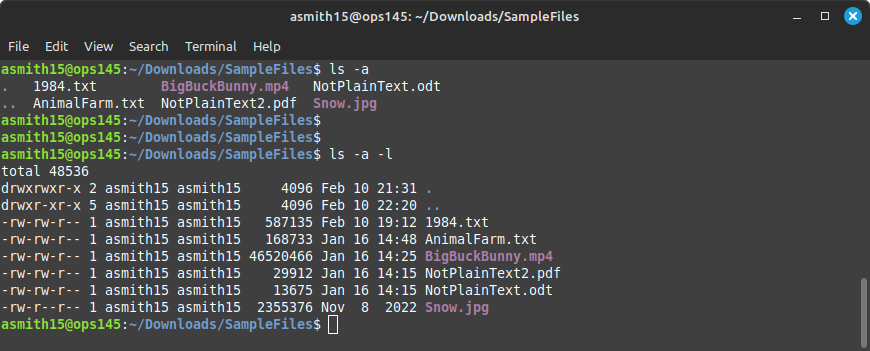
You can see these records when you run ls with the -a argument. Let's look at the SampleFiles directory you downloaded back in Lab 2:
- Open a terminal, and change the PWD to ~/Downloads/SampleFiles
- Run ls -a Note that in the output there is a . and a ..
- Run ls -a -l Note that the . and .. are directories.
- Remember that you can give an argument to ls telling it to show the details of a specific file or directory. For example ls -l 1984.txt will show details about that specific file, and ls -l / will show details for the immediate contents of the root directory.
- Run ls -l -a . (including the dot in the end) and note that it shows the same output as ls -l -a That's because:
- ls will show the contents of PWD if you don't give it a specific path.
- Your PWD is ~/Downloads/SampleFiles/
- The . in SampleFiles points to itself (SampleFiles)
- Run ls -l -a .. and ls -l -a ~/Downloads Note that the output is the same. That's because:
- Your PWD is ~/Downloads/SampleFiles/
- The parent directory of ~/Downloads/SampleFiles/ is ~/Downloads/
- Inside ~/Downloads/SampleFiles/ .. and ~/Downloads are the same thing
- The same for every other directory. The only sort-of exception is the root directory. Because it's the root and it doesn't have a parent: its parent is itself:
- Take some time to look at these many lines and understand that actually it's not that complicated. You just have to remember: dot is for itself, dot-dot is for its parent.
Hidden files
Dots have another (mostly unrelated) special use when it comes to filesystems in the shell. Any file/directory name which begins with a dot is considered hidden.
This is definitely not a security feature! It is purely a convenience.
- Change your PWD to your home directory.
- Run ls
- Run ls -a
Notice there are many more files and directories in your home than you saw before. These were always there, the ls command doesn't show them by default. The -a argument tells ls to also show hidden files.
These are hidden to avoid clutter, to make it easier for you to find things you want. There's nothing special about these files and directories. They're just rarely manipulated by users.
This is also where the "extension" idea breaks down completely. If you insist that a file's extension is everything after the dot and the file's name is everything before the dot: all these hidden files have no names, and only extensions. That's clearly not the case. Almost all these files are plain text files, without a .txt extension.
- Use the cat command to look at the contents of .bash_history. This file is where the commands you ran previously are stored, so you can retrieve them using the arrow keys.
- Since you're at it: here's a new command. Run history on the terminal. It will show you all the previous commands you've run.
The * wildcard
You've used the * wildcard (called a star, it's the multiplication sign on your keyboard) in lab 3 to delete several files at the same time. Now we'll look at it in more detail.
Sometimes you want to do something will all the contents of a directory. At other times you might want to do something with all your .jpg files, or all the .txt files, or all the files which have backup in their name. Those are examples of when you use a *
- Now that you're more comfortable with the command-line: download and extract the next tarball using commands instead of Firefox and a graphical archive manager:
cd ~/Downloads # To make sure it's downloaded here ls -l -h # To confirm you didn't already download SpecialChars.tar.xz wget http://ops345.ca/ops145/SpecialChars.tar.xz # This will download SpecialChars.tar.xz into the PWD tar xvf SpecialChars.tar.xz # This will extract the contents of SpecialChars.tar.xz into the PWD
Inside the newly created ~/Downloads/SpecialChars/ directory is a SortMe subdirectory, which is a disorganized mess. Let's organize it. Remember that the whole point is to learn wildcards, so use commands in a terminal to move files around instead of dragging them in the graphical interface.
- Use the graphical file manager to look at the SortMe directory to get an idea of what's in there. Note that:
- There are pictures and sounds
- Some of the pictures are small squares, and others are large photos
- Some of the sounds are .wav files and others are .oga files
- Some of the .wav files sound like speaker test sounds
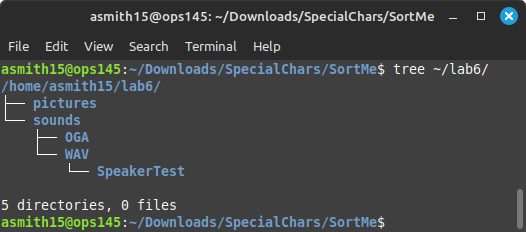
- We're going to organize these into the following directory tree inside ~/lab6:
- Remember that filenames are case-sensitive. Open a terminal and create the directory tree above using as many commands as you like. But here's a handy argument you can give to the mkdir command: -pWhen run with -p, the mkdir command will create not only the last directory on the path you give it, but all the other missing directories in that path as well. You might want to avoid using this if you're not very comfortable with the command-line yet, since it's very easy to create a hundred directories in the wrong place by giving mkdir -p the wrong path several times.
mkdir -p ~/lab6/sounds/WAV/SpeakerTest
- Change your PWD to ~/Downloads/SpecialChars/SortMe
When the bash shell encounters a * character on the command-line: it assumes you're trying to use it as a wildcard for filenames, and does its best to replace the * with a list of all filenames which match the pattern.
On its own: a * matches any number of any characters. We can test this easily using the ls command:
ls *
This appears to print the same output as ls on its own, but in fact the ls command received from the shell a list of all the files in ~/Downloads/SpecialChars/SortMe as arguments. You can combine the * wildcard with other characters, restricting what it will be expanded to. For example:
ls *jpg
This time * still expands to anu number of any characters, but because it's combined with an explicit jpg in the end: the result will be a list of all the files which have jpg at the end of their name.
- Try running commands similar to the above with different extensions.
The wildcard doesn't have to be at the beginning. It can be in the end. For example this is how you would get a list of all the files which have names starting with amanea:
ls amanea*
The wildcard can be in the middle too. For example this is how you would get a list of all the files with _ somewhere in the name:
ls *_*
Or a list of filenames which contain an _ and end with wav:
ls *_*wav
- all .png files
- all .jpg and .JPG files
- ls *log*
- all access_log* files
Comments
Special characters
- wget/tar instead of firefox/archivemanager
- * and ? wildcards
- spaces in filenames
- single quotes
- double quotes
- \
- Back-quote does something else
- Revisit ls, cat, mkdir, rm, mv, cp with spaces and special characters
- Mismatched quotes
- Quotes to work with filenames with special characters, and other quotes